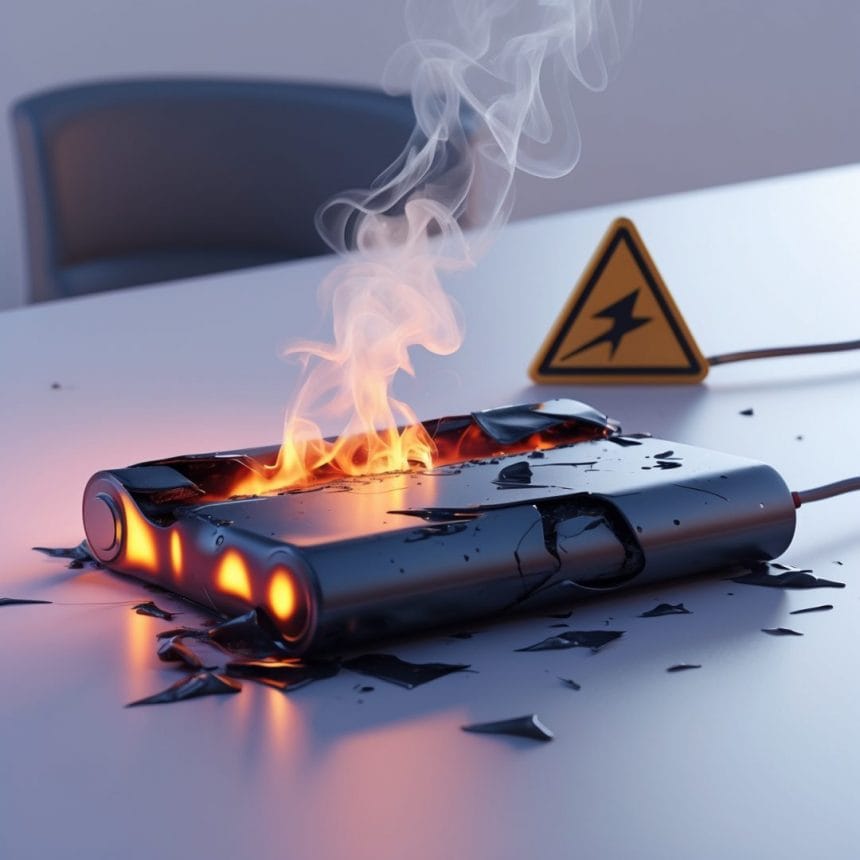
While this sounds alarming, it’s important to understand the causes of lithium battery explosions and why lithium batteries explode, so we can use them more safely and confidently. This article explores the science behind these rare but real incidents, the most common risk factors, and how to protect yourself without fearing your devices.
The Science Behind Battery Fires
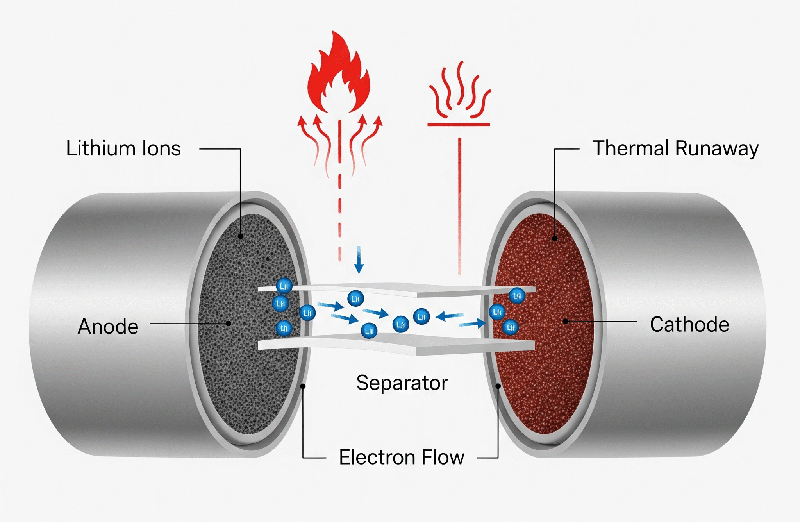
At the core of a lithium-ion battery is a delicate balance of chemistry. These batteries work by moving lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging, but improper handling can increase the risk of lithium battery explosions. However, this process involves flammable electrolytes, and when something goes wrong—such as physical damage, overheating, or internal short circuits—it can trigger a chain reaction known as thermal runaway, which is one of the main reasons behind lithium battery explosions.
Thermal runaway is the point where the battery’s temperature rapidly increases, causing internal pressure to build. If this pressure can’t be relieved, the battery swells, leaks, or in the worst-case scenario, explodes. This chain reaction can be initiated by something as simple as leaving a device in a hot car or using a faulty charger.
What Usually Causes Lithium Battery Explosions?
Most lithium battery explosions and failures come down to one of the following causes:
- Overcharging: Using an improper charger or leaving a battery plugged in too long can lead to heat buildup.
- Physical damage: Dropping your phone or crushing a battery can damage internal structures, creating short circuits.
- Manufacturing defects: Poor quality control, especially in cheaper devices, can lead to microscopic flaws that grow over time.
- Improper storage: Storing batteries in hot environments or near metal objects can create risks.
Though modern batteries have built-in safety mechanisms, they are not fail-proof. In fact, some well-known lithium battery fire incidents—including the Samsung Galaxy Note 7 recall and several e-scooter explosions—stemmed from design flaws or overlooked hazards.
How to Use Lithium Batteries Safely: Practical Tips for Everyday Devices
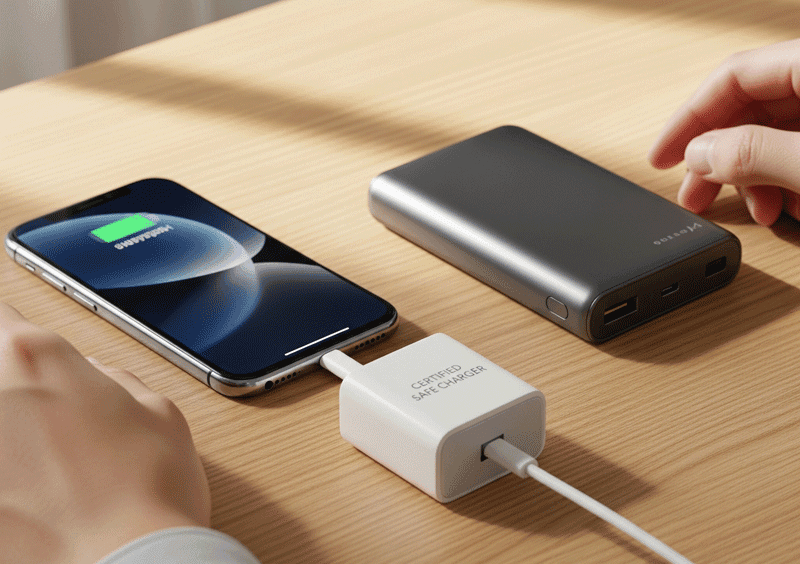

The good news is, with a few simple precautions, the risk of lithium battery explosions can be dramatically reduced. Here are some practical, science-backed ways to protect yourself and extend the life of your devices:
1. Avoid Extreme Temperatures
Never leave devices in hot cars or under direct sunlight. High heat is a major trigger for thermal runaway. Similarly, freezing temperatures can cause battery stress, especially when recharging.
2. Use Certified Chargers and Cables
Off-brand chargers might be cheaper, but they often lack proper voltage regulation. Always use the charger that comes with your device or a reputable certified alternative to avoid overcharging or short circuits.
3. Don’t Charge Overnight if It’s Not Necessary
Modern phones stop charging once full, but prolonged heat from overnight charging may still degrade the battery over time. If you must charge overnight, place your phone on a heat-dissipating surface—not under a pillow or blanket.
4. Replace Swollen Batteries Immediately
A bulging phone back or a laptop that won’t sit flat could signal a swollen battery—a clear warning sign. Continuing to use it could result in leakage or fire. Replace it through an authorized service center as soon as possible.
5. Store Spare Batteries Safely
If you’re storing lithium batteries—like for power banks, drones, or cameras—keep them in a cool, dry place. Avoid contact with metal objects (like keys or coins), and use a battery case to prevent accidental discharge.
These simple habits not only reduce risks but also prolong your battery’s lifespan, saving you money and unnecessary danger.
The Future of Battery Safety
Battery technology is evolving rapidly to address challenges like lithium battery explosions. One of the most promising developments is the shift toward solid-state batteries, which replace the flammable liquid electrolyte with a solid material. These designs are far less likely to overheat or catch fire, and they offer higher energy density—meaning longer-lasting power in a smaller package.
Companies like Toyota and QuantumScape are already working on commercial solid-state solutions, and within the next few years, we may see these safer lithium battery alternatives powering everything from smartphones to EVs.
Until then, awareness and good habits remain our best tools.
Final Thoughts
Lithium-ion batteries have revolutionized modern life, but they’re not without risks. Understanding how they work, what causes lithium battery explosions, and how to handle them responsibly can help you stay safe without giving up the convenience they offer.
So next time you charge your phone, store a power bank, or buy a new gadget, remember: a little caution goes a long way when it comes to battery safety.