Nuclear fusion is one of the most promising energy technologies in the world. It is the same process that powers the Sun and other stars, and scientists hope it could one day provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on Earth. The idea is simple in principle but extremely difficult in practice: recreate star-like conditions, control the reaction, and produce more usable energy than the system consumes.
In this guide, we explain what nuclear fusion is, how it works, why it matters, what is slowing it down, and what recent breakthroughs actually mean for the future of energy.
What Is Nuclear Fusion?
At its core, nuclear fusion is the process of combining two light atomic nuclei into a heavier nucleus. When that happens, a portion of mass is converted into energy, releasing a very large amount of heat.
This is the opposite of nuclear fission, which releases energy by splitting heavy atoms such as uranium. Fusion is what happens naturally in stars, where extreme heat and pressure force hydrogen nuclei to fuse and form helium.
On Earth, the most commonly studied fusion reaction for power generation uses the hydrogen isotopes deuterium and tritium. When they fuse, they produce helium, a neutron, and a large burst of energy.
How Does Nuclear Fusion Work?
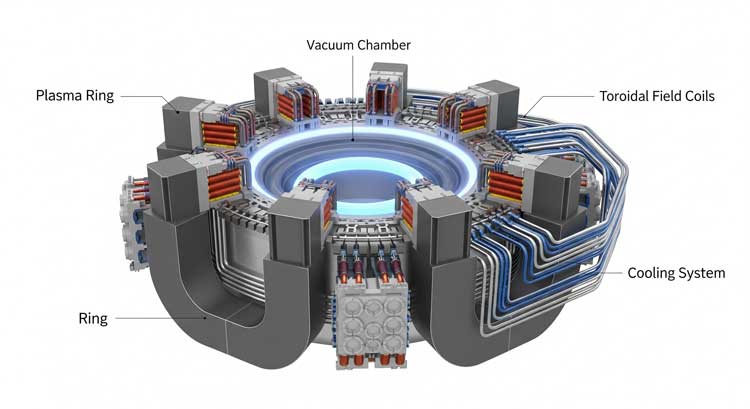
To create nuclear fusion on Earth, scientists must generate and control extreme conditions similar to those inside stars. That usually means heating fuel to temperatures above 100 million degrees Celsius, turning it into a superheated state called plasma.
There are two main approaches used in fusion research today:
- Magnetic confinement fusion, which uses strong magnetic fields to contain plasma (for example, tokamaks and stellarators).
- Inertial confinement fusion, which uses powerful lasers to compress and heat a tiny fuel pellet for a very short time.
Here is a simplified step-by-step version of how fusion works in a reactor system:
1. Heating the Fuel
Fusion fuel, usually deuterium and tritium, is heated until it becomes plasma. In this state, electrons are stripped from atoms, and the fuel can be manipulated by magnetic fields.
2. Confining the Plasma
The plasma must be kept hot and stable long enough for fusion to occur. In tokamaks, strong magnetic fields keep the plasma away from reactor walls. In laser-based systems, intense laser pulses compress the fuel to extremely high density for a brief moment.
3. Fusing the Nuclei
If temperature, pressure, and confinement are sufficient, hydrogen nuclei collide and fuse into helium. This releases energy as heat and fast neutrons.

4. Capturing the Energy
In a future fusion power plant, the released energy would heat a coolant, create steam, and drive a turbine to generate electricity, similar to other thermal power plants. This part is familiar engineering. The difficult part is sustaining the fusion reaction efficiently and reliably.
Why Is Nuclear Fusion So Important?
1. Low-Carbon Power Generation
Fusion itself does not burn fossil fuels, so it does not produce carbon dioxide during power generation. That makes nuclear fusion attractive as a potential long-term clean energy source if it becomes commercially viable.
2. High Energy Density
Fusion reactions release enormous energy from very small amounts of fuel. In theory, this could provide stable, high-output electricity without the land footprint required by some other energy systems.
3. Abundant Fuel Inputs
Deuterium can be extracted from water, and tritium can be produced from lithium in reactor systems. These fuel sources are one reason fusion is often described as a long-term energy option with strong supply potential.
4. Different Safety Profile Than Fission
Fusion reactors do not operate like fission reactors. They do not rely on a self-sustaining chain reaction in the same way. If plasma control is lost, the fusion reaction stops rather than escalating. This gives fusion an important safety advantage in principle, although it still involves complex engineering and radiation management challenges.

What Are the Main Challenges of Fusion Energy?
Despite decades of progress, fusion is still not a commercial power source. The reason is straightforward: nuclear fusion is scientifically possible, but engineering it into a reliable and affordable power plant is extremely hard.
- Extreme temperatures and stability: Plasma must remain hot and stable under difficult conditions, and small instabilities can disrupt the reaction.
- Confinement efficiency: The plasma must be confined long enough and densely enough for useful fusion output.
- Materials stress: Reactor components face intense heat and neutron bombardment, which can damage materials over time.
- Tritium handling and fuel cycle complexity: Tritium is radioactive and must be managed carefully in practical reactor designs.
- Cost and scale: Fusion systems require advanced magnets, lasers, cryogenic systems, and precision engineering, which are currently expensive.
Another major issue is the difference between a scientific milestone and a commercial energy system. A fusion experiment may show an important physics breakthrough, but that does not automatically mean a grid-ready power plant is close.
Recent Fusion Breakthroughs, What They Mean (and What They Do Not)
Fusion research has made real progress in recent years, including major milestones in plasma performance and laser-driven fusion experiments. One widely reported breakthrough was the U.S. National Ignition Facility’s fusion ignition result, which demonstrated that fusion energy output exceeded the laser energy delivered to the target in that experiment.
That was an important scientific achievement, but it should be understood correctly. It did not mean a fusion power plant is already producing net electricity for the grid. There is still a large gap between laboratory ignition and a repeatable, economical power system.
This distinction matters because fusion headlines are often accurate but oversimplified. Progress is real, but commercialization still requires years of engineering advances, cost reduction, and large-scale system integration.
Nuclear Fusion vs Nuclear Fission
People often compare fusion and fission because both are nuclear technologies, but they work differently and have different trade-offs.
- Fission: Splits heavy atoms (like uranium), used in current nuclear power plants.
- Fusion: Combines light atoms (like hydrogen isotopes), still in the development stage for power generation.
- Fission waste: Produces long-lived radioactive waste that requires long-term management.
- Fusion waste profile: Different and generally less long-lived than fission fuel waste, but still requires radiation-aware materials handling.
- Commercial status: Fission is commercial now, fusion is not yet commercial at utility scale.
Is Nuclear Fusion the Future of Energy?

Nuclear fusion is a strong candidate for part of the future energy mix, but it is not a near-term replacement for existing power systems. A realistic view is that fusion could become an important long-term source of firm, low-carbon electricity if current research and engineering efforts continue to succeed.
Governments, national labs, and private companies are investing heavily in fusion technologies, including tokamaks, stellarators, and newer reactor concepts. Projects such as ITER and private-sector programs are pushing the field forward, but commercial timelines remain uncertain and should be treated cautiously.
If fusion reaches practical deployment, it could complement renewables like solar and wind by providing steady power when weather conditions are not ideal. That is one reason fusion remains a serious strategic technology, not just a scientific curiosity.
Did you know nuclear fusion research has also inspired discussions about element transmutation, including turning mercury into gold? While this is not a practical way to create wealth, it is a fascinating example of how nuclear science can change atomic structure. Read more about the theory here.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is nuclear fusion available today?
Not as a mainstream commercial electricity source. Fusion is still in the research and demonstration stage, although progress has accelerated.
Is fusion cleaner than fossil fuels?
Yes, fusion does not burn fossil fuels and does not produce carbon emissions during power generation. It is considered a potential low-carbon energy source.
Can a fusion reactor melt down?
Fusion reactors have a different safety profile than fission reactors. If operating conditions are lost, the fusion reaction stops rather than continuing as a runaway chain reaction.
Why is fusion taking so long?
Because it requires extreme temperatures, stable plasma control, advanced materials, and very complex engineering, all at a cost that must eventually work for real power plants.
Conclusion: A Star-Powered Future?
Nuclear fusion is real, scientifically proven, and increasingly credible as a future energy technology. But it is not a solved commercial product yet. The field is moving forward through hard engineering progress, not magic headlines.
If researchers and companies can make fusion systems reliable, scalable, and affordable, fusion could become one of the most important clean energy breakthroughs of this century. Until then, it remains one of the most ambitious and worthwhile bets in modern science and energy innovation.